SASS预处理器
什么是CSS预处理器
CSS预处理器是一种脚本语言,是CSS的扩展。它被编译成常规的CSS语法,然后由Web浏览器读取CSS。较少看起来与CSS非常相似,但它提供了诸如变量,函数,混合和操作等功能,可以帮助您构建动态CSS。
常用的CSS预处理器有哪些
目前前端开发人员使用的3种最流行的CSS预处理器,即Sass、LESS和Stylus。
由来不在阐述,感兴趣的可以网上看下资料
Sass安装
如何安装Sass
Sass语法嵌套规则
选择器嵌套
例如有这么一段css,正常CSS的写法
1
2
3
4
5
| .container{width:1200px; margin: 0 auto;}
.container .header{height: 90px; line-height: 90px;}
.container .header .log{width:100px; height:60px;}
.container .center{height: 600px; background-color: #F00;}
.container .footer{font-size: 16px;text-align: center;}
|
改成写SASS的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| .container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
.header {
height: 90px;
line-height: 90px;
.log {
width: 100px;
height: 60px;
}
}
.center {
height: 600px;
background-color: #F00;
}
.footer {
font-size: 16px;
text-align: center;
}
}
|
避免了重复输入父选择器,复杂的 CSS 结构更易于管理
父选择器 &
在嵌套 CSS 规则时,有时也需要直接使用嵌套外层的父选择器,例如,当给某个元素设定 hover 样式时,或者当 body 元素有某个 classname 时,可以用 & 代表嵌套规则外层的父选择器。
例如有这么一段样式:
1
2
3
4
5
| .container{width: 1200px;margin: 0 auto;}
.container a{color: #333;}
.container a:hover{text-decoration: underline;color: #F00;}
.container .top{border:1px #f2f2f2 solid;}
.container .top-left{float: left; width: 200px;}
|
用sass编写
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| .container {
width: 1200px;
margin: 0 auto;
a {
color: #333;
&:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
color: #F00;
}
}
.top {
border: 1px #f2f2f2 solid;
&-left {
float: left;
width: 200px;
}
}
}
|
SASS变量
CSS定义变量的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| :root {
--color: #F00;
}
body {
--border-color: blue;
}
.header {
--background-color: #f8f8f8;
}
p {
color: var(--color);
border: 1px solid var(--border-color);
}
.header {
background-color: var(--background-color);
}
|
SASS的写法
1
2
3
4
| $font-size: 14px;
.container {
font-size: $font-size;
}
|
局部变量
定义:在选择器内容定义的变量,只能在选择器范围内使用
1
2
3
4
| .container {
$font-size: 14px;
font-size: $font-size;
}
|
全局变量
定义后能全局使用的变量
第一种:在选择器外面的最前面定义的变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| $font-size:16px;
.container {
font-size: $font-size;
}
.footer {
font-size: $font-size;
}
|
第二种:使用 !global 标志定义全局变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| .container {
$font-size: 16px !global;
font-size: $font-size;
}
.footer {
font-size: $font-size;
}
|
#####变量值类型
变量值的类型可以有很多种
SASS支持 7 种主要的数据类型
- 数字,1, 2, 13, 10px,30%
- 字符串,有引号字符串与无引号字符串,”foo”, ‘bar’, baz
- 颜色,blue, #04a3f9, rgba(255,0,0,0.5)
- 布尔型,true, false
- 空值,null
- 数组 (list),用空格或逗号作分隔符,1.5em 1em 0 2em, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif
- maps, 相当于 JavaScript 的 object,(key1: value1, key2: value2)
例如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| $layer-index:10;
$border-width:3px;
$font-base-family:'Open Sans', Helvetica, Sans-Serif;
$top-bg-color:rgba(255,147,29,0.6);
$block-base-padding:6px 10px 6px 10px;
$blank-mode:true;
$var:null;
$color-map: (color1: #fa0000, color2: #fbe200, color3: #95d7eb);
$fonts: (serif: "Helvetica Neue",monospace: "Consolas");
|
###SASS 导入@import
@import,允许其导入 SCSS 或 Sass 文件
例子:
public.scss
在index.scss里面使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @import "public";
$color:#666;
.container {
border-color: $color;
color: $font-base-color;
}
|
注意:跟我们普通css里面@import的区别
如下几种方式,都将作为普通的 CSS 语句,不会导入任何 Sass 文件
- 文件拓展名是 .css;
- 文件名以 http:// 开头;
- 文件名是 url();
- @import 包含 media queries。
1
2
3
4
| @import "public.css";
@import url(public);
@import "http://xxx.com/xxx";
@import 'landscape' screen and (orientation:landscape);
|
定义混合指令 @mixin1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@mixin block {
width: 96%;
margin-left: 2%;
border-radius: 8px;
border: 1px #f6f6f6 solid;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
.container {
.block {
@include block;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@mixin block-padding($top, $right, $bottom: 10px, $left: 5) {
padding-top: $top;
padding-right: $right;
padding-bottom: $bottom;
padding-left: $left;
}
|
1
2
3
4
|
.container {
@include block-padding(10px, 20px, 30px, 40px);
}
|
- 混合指令是可以重复使用的一组CSS声明
- 混合指令有助于减少重复代码,只需声明一次,就可在文件中引用
- 混合指令可以包含所有的 CSS 规则,绝大部分 Sass 规则,甚至通过参数功能引入变量,输出多样化的样式。
- 使用参数时建议加上默认值
@extend(继承)指令
在设计网页的时候通常遇到这样的情况:一个元素使用的样式与另一个元素完全相同,但又添加了额外的样式。通常会在 HTML 中给元素定义两个 class,一个通用样式,一个特殊样式。
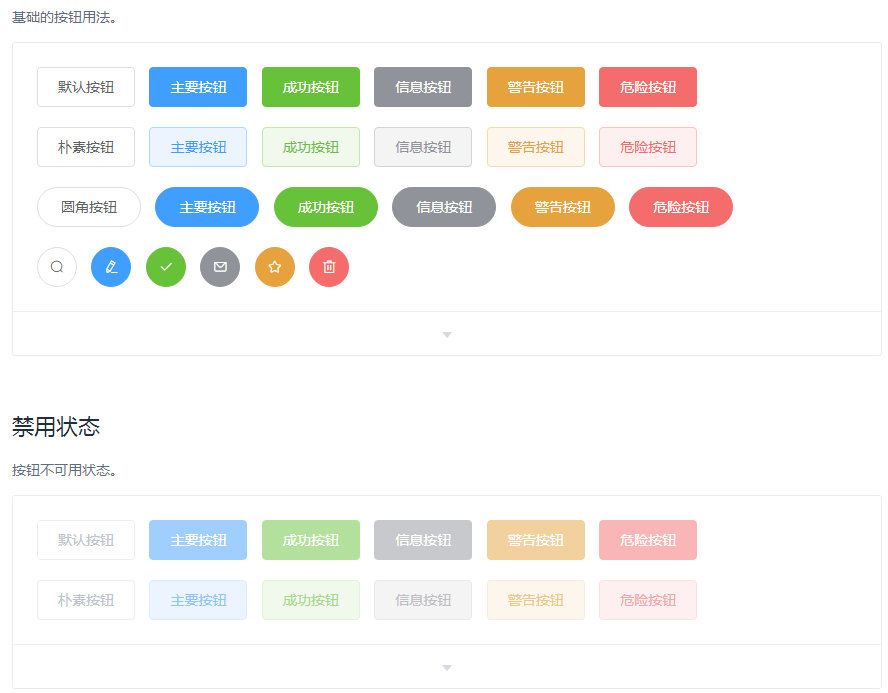
####CSS案例
接下来以警告框为例进行讲解4种类型
| 标记 |
说明 |
| info |
信息!请注意这个信息。 |
| success |
成功!很好地完成了提交。 |
| warning |
警告!请不要提交。 |
| danger |
错误!请进行一些更改。 |
所有警告框的基本样式(风格、字体大小、内边距、边框等…) ,因为我们通常会定义一个通用alert样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| .alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
|
不同警告框单独风格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| .alert-info {
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <div class="alert alert-info">
信息!请注意这个信息。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-success">
成功!很好地完成了提交。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-warning">
警告!请不要提交。
</div>
<div class="alert alert-danger">
错误!请进行一些更改。
</div>
|
使用继承@extend改进
基本样式我们没有变,主要是各个警告框单独的样式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| .alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.alert-info {
@extend .alert;
color: #31708f;
background-color: #d9edf7;
border-color: #bce8f1;
}
.alert-success {
@extend .alert;
color: #3c763d;
background-color: #dff0d8;
border-color: #d6e9c6;
}
.alert-warning {
@extend .alert;
color: #8a6d3b;
background-color: #fcf8e3;
border-color: #faebcc;
}
.alert-danger {
@extend .alert;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}
|
使用时就不须要再写基本类了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <div class="alert-info">
信息!请注意这个信息。
</div>
<div class="alert-success">
成功!很好地完成了提交。
</div>
<div class="alert-warning">
警告!请不要提交。
</div>
<div class="alert-danger">
错误!请进行一些更改。
</div>
|
####使用多个@extend
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| .alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.important {
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 14px;
}
.alert-success {
@extend .alert;
@extend .important;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}
|
####@extend多层继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| .alert {
padding: 15px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 12px;
}
.important {
@extend .alert;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 14px;
}
.alert-success {
@extend .important;
color: #a94442;
background-color: #f2dede;
border-color: #ebccd1;
}
|
###运算符的基本使用
等号运行符
所有数据类型都支持等号运算符:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
$theme:1;
.container {
@if $theme == 1 {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}
$theme:"blue";
.container {
@if $theme != "blue" {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}
|
比较运行符
| 大于
<= | 小于等于
= | 大于等于
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| $theme:3;
.container {
@if $theme >= 5 {
background-color: red;
}
@else {
background-color: blue;
}
}
|
逻辑运行符
| 符号 |
说明 |
| and |
逻辑与 |
| or |
逻辑或 |
| not |
逻辑非 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| $width:100;
$height:200;
$last: false;
div {
@if $width>50 and $height<300 {
font-size: 16px;
}
@else {
font-size: 14px;
}
@if not $last {
border-color: red;
}
@else {
border-color: blue;
}
}
|
数字操作符
符号 | 说明
— | :—
- | 乘
/ | 除
% | 取模1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
.container {
width: 50 + 20;
width: 50 + 20%;
width: 50% + 20%;
width: 10px + 20px;
width: 10pt + 20px;
width: 10pt + 20;
width: 10px + 10;
height: 50 - 30;
height: 10 - 30%;
height: 60% - 30%;
height: 50px - 20px;
height: 50pt - 20px;
height: 50pt - 40;
height: 50 * 30;
height: 10 * 30%;
height: 50 * 2px;
height: 50pt * 4;
$width: 100px;
width: 10 / 5;
width: 10px / 5px;
width: 10px / 10 * 2;
width: 20px / 2px * 5%;
width: ($width/2);
z-index: round(10)/2;
height: (500px/2);
width: 10 % 3;
width: 50 % 3px;
width: 50px % 4px;
width: 50px % 7;
width: 50% % 7;
width: 50% % 9%;
width: 50px % 10pt;
width: 50px % 13.33333px;
width: 50px + 10pt;
}
|
- 如果值或值的一部分,是变量或者函数的返回值
- 如果值被圆括号包裹
- 如果值是算数表达式的一部分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| $width: 1000px;
div {
font: 16px/30px Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
width: ($width/2);
z-index: round(10)/2;
height: (500px/2);
margin-left: 5px + 8px/2px;
}
|
插值语句 #{ }
引入之前的案例发出一个问题
1
2
3
| p{
font: 16px/30px Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
}
|
如果需要使用变量,同时又要确保 / 不做除法运算而是完整地编译到 CSS 文件中,只需要用 #{} 插值语句将变量包裹。
使用插值语法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| p {
$font-size: 12px;
$line-height: 30px;
font: #{$font-size}/#{$line-height} Helvetica,
sans-serif;
}
|
通过 #{} 插值语句可以在选择器、属性名、注释中使用变量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| $class-name: danger;
$attr: color;
$author:'老姚';
a.#{$class-name} {
border-#{$attr}: #F00;
}
|
sass 常见函数的基本使用
常见函数简介,更多函数列表可看:https://sass-lang.com/documentation/modules
Map函数
Map函数操作Map,map-get()根据键值获取map中的对应值,map-merge()来将两个map合并成一个新的map,map-values()映射中的所有值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| $font-sizes: ("small": 12px, "normal": 18px, "large": 24px);
$padding:(top:10px, right:20px, bottom:10px, left:30px);
p {
font-size: map-get($font-sizes, "normal");
@if map-has-key($padding, "right") {
padding-right: map-get($padding, "right");
}
&:after {
content: map-keys($font-sizes) + " "+ map-values($padding) + "";
}
}
|
###流程控制指令@if、@for、@each、@while
####@if控制指令
@if()函数允许您根据条件进行分支,并仅返回两种可能结果中的一种。
语法方式同js的if….else if …else
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| $theme:"green";
.container {
@if $theme=="red" {
color: red;
}
@else if $theme=="blue" {
color: blue;
}
@else if $theme=="green" {
color: green;
}
@else {
color: darkgray;
}
}
|
实例,定义一个css的三角形@mixin声明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| @mixin triangle($direction:top, $size:30px, $border-color:black) {
width: 0px;
height: 0px;
display: inline-block;
border-width: $size;
border-#{$direction}-width: 0;
@if ($direction==top) {
border-color: transparent transparent $border-color transparent;
border-style: dashed dashed solid dashed;
}
@else if($direction==right) {
border-color: transparent transparent transparent $border-color;
border-style: dashed dashed dashed solid;
}
@else if($direction==bottom) {
border-color: $border-color transparent transparent transparent;
border-style: solid dashed dashed dashed;
}
@else if($direction==left) {
border-color: transparent $border-color transparent transparent;
border-style: dashed solid dashed dashed;
}
}
.p0 {
@include triangle();
}
.p1 {
@include triangle(right, 50px, red);
}
.p2 {
@include triangle(bottom, 50px, blue);
}
.p3 {
@include triangle(left, 50px, green);
}
|
1
2
3
4
| <p class="p0"></p>
<p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2"></p>
<p class="p3"></p>
|
####@for指令
@for 指令可以在限制的范围内重复输出格式,每次按要求(变量的值)对输出结果做出变动。这个指令包含两种格式:@for $var from through ,或者 @for $var from to
区别在于 through 与 to 的含义:
当使用through时,条件范围包含与的值。
而使用to 时条件范围只包含的值不包含 的值。
另外,$var 可以是任何变量,比如 $i; 和 必须是整数值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @for $i from 1 to 4 {
.p#{$i} {
width: 10px * $i;
height: 30px;
background-color: red;
}
}
@for $i from 1 through 3 {
.p#{$i} {
width: 10px * $i;
height: 30px;
background-color: red;
}
}
|
1
2
3
| <p class="p1"></p>
<p class="p2"></p>
<p class="p3"></p>
|
####@each指令
@each 指令的格式是 $var in , $var 可以是任何变量名,比如 $length 或者 $name,而 是一连串的值,也就是值列表。
例如做如下效果

普通CSS的写法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| p{
width: 10px;
height: 10px;
display: inline-block;
margin: 10px;
}
.p0{
background-color: red;
}
.p1{
background-color: green;
}
.p2{
background-color: blue;
}
.p3{
background-color:turquoise;
}
.p4{
background-color: darkmagenta;
}
|
用@each改进
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| $color-list:red green blue turquoise darkmagenta;
@each $color in $color-list {
$index: index($color-list, $color);
.p#{$index - 1} {
background-color: $color;
}
}
|
####@while 指令
@while 指令重复输出格式直到表达式返回结果为 false。这样可以实现比 @for 更复杂的循环。
用sass实现bootstrap中css的这么一段代码
https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.4.1/css/bootstrap.css
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| .col-sm-12 {
width: 100%;
}
.col-sm-11 {
width: 91.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-10 {
width: 83.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-9 {
width: 75%;
}
.col-sm-8 {
width: 66.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-7 {
width: 58.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-6 {
width: 50%;
}
.col-sm-5 {
width: 41.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-4 {
width: 33.33333333%;
}
.col-sm-3 {
width: 25%;
}
.col-sm-2 {
width: 16.66666667%;
}
.col-sm-1 {
width: 8.33333333%;
}
|
用@while实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| $column:12;
@while $column>0 {
.col-sm-#{$column} {
width: $column / 12 * 100%;
width: $column / 12 * 100#{"%"};
width: unquote($string: $column / 12 * 100 + "%");
}
$column:$column - 1;
}
|
####三元条件函数if的使用
if的写法(浅色与深色模式)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| $theme:'light';
.container {
@if $theme=='light' {
color: #000;
}
@else {
color: #FFF;
}
}
|
三元条件函数if改进
1
2
3
4
| $theme:'light';
.container {
color: if($theme=='light', #000, #FFF);
}
|






